Pregnancy Screening 2024
Screening of pregnant women, 2024
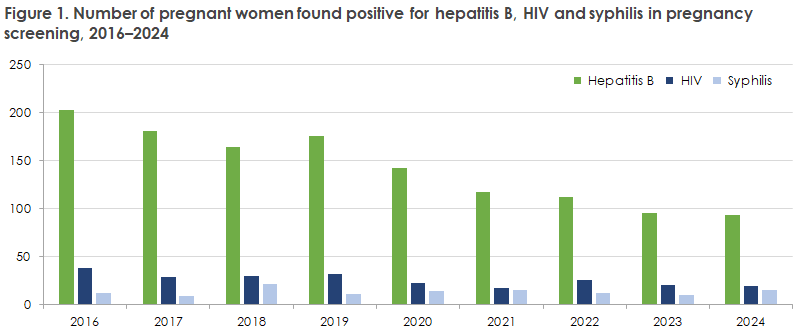
In 2024, 65,331 blood type analyses were performed among pregnant women. Almost all of these (99.9%) were tested for hepatitis B virus, HIV and syphilis.
Pregnant women with HIV
In 2024, 19 women were found to have HIV in the pregnancy screening (0.03% of those tested). Among these, 3 women were newly diagnosed with HIV, and 16 were known HIV-positive.
None of the pregnant women with newly diagnosed HIV were Danish (two were from Ukraine and one was from Kenya). Two of the pregnant women with known HIV were Danish, while the remaining were predominantly from sub-Saharan Africa.
Pregnant women with syphilis
A total of 109 pregnant women tested positive in the syphilis screening test in 2024. Confirmatory serological tests were performed on 106 of the women (97%). The confirmatory test makes it possible to identify both false positives/previously infected women and those with active syphilis. The majority of the 106 were false positives or had antibodies from previous syphilis infection. Fifteen were found to have active syphilis, corresponding to 0.02% of all screened pregnant women. For the remaining three, no confirmatory test was performed, despite several contacts from Statens Serum Institut and/or their general practitioner.
Pregnant women with hepatitis B
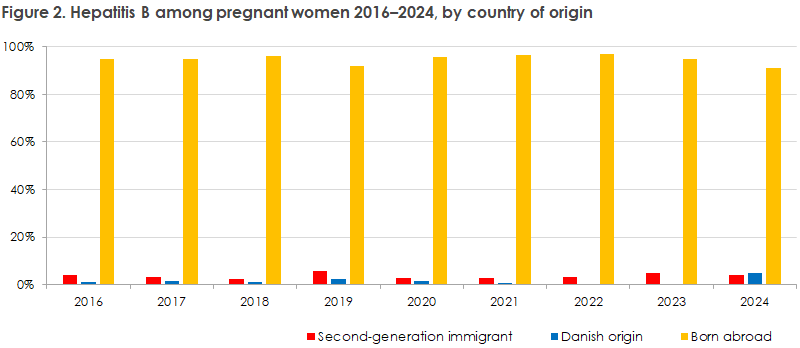
Of the 65,261 pregnant women who were tested for hepatitis B, 93 (0.14%) were positive for HBsAg (hepatitis B surface antigen), which is at the same level as last year, see Figure 1. Of these, 71 women were already known to have hepatitis B, and 22 were found positive for the first time in the pregnancy screening.
91% of the pregnant women who tested positive for hepatitis B were born abroad. The most frequent countries of origin among pregnant women with hepatitis B were China, Romania, the Philippines, Somalia and Vietnam. This reflects the distribution of hepatitis B prevalence in the Danish population. The remaining 4% were either second-generation immigrants (4%) or of Danish origin (5%) – all born before the introduction of the general screening of pregnant women for hepatitis B in 2005.
HIV
Also for HIV among pregnant women, there is a considerable predominance of women born abroad, see Figure 3. In contrast, there are almost no second-generation immigrants with HIV in the pregnancy screening.

Syphilis
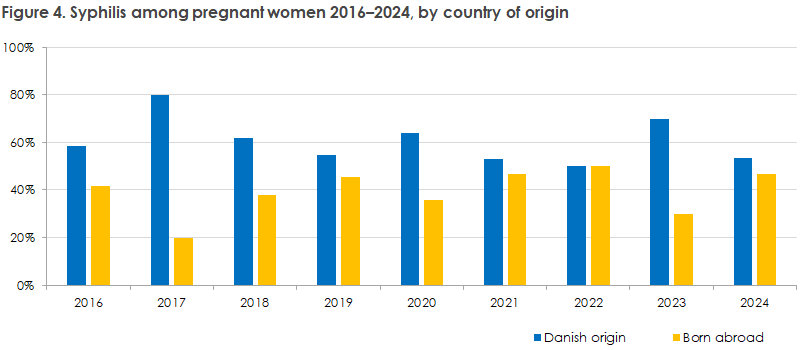
In contrast to hepatitis B and HIV, a considerable proportion of women born in Denmark were seen with syphilis found in the pregnancy screening, see Figure 4. In 2024, however, the distribution was more evenly divided between persons born in Denmark (53%) and persons born abroad (47%).
This report is also mentioned in EPI-NEWS 45/2025.