MRSA 2024
MRSA – disease occurrence 2024
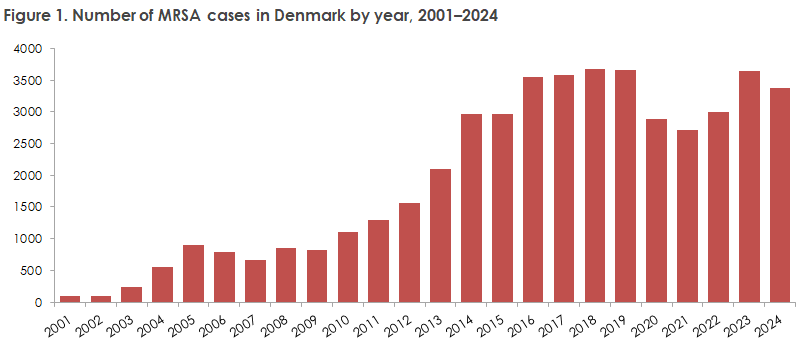
In 2024, 3,372 individuals were registered as having methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Thus, the number was slightly lower than in 2023 but at the same level as in the years before the COVID-19 pandemic, during which the number fell by approximately 20% due to restrictions on international travel and social contact.
Epidemiological classification
MRSA cases are classified according to presumed mode of transmission as imported (foreign-acquired), hospital-acquired, community-acquired, and livestock-associated. Livestock-associated
MRSA in Denmark is almost always of the MRSA type CC398, which is closely linked to contact with live pigs, whereas the other presumed transmission categories involve many different MRSA types.
Community-acquired MRSA cases are further subdivided according to whether the person has had contact with hospitals or the nursing home sector within the previous six months, and whether the person has had known exposure to a person with MRSA.
Table 1 shows the distribution of reported MRSA cases by presumed route of transmission.
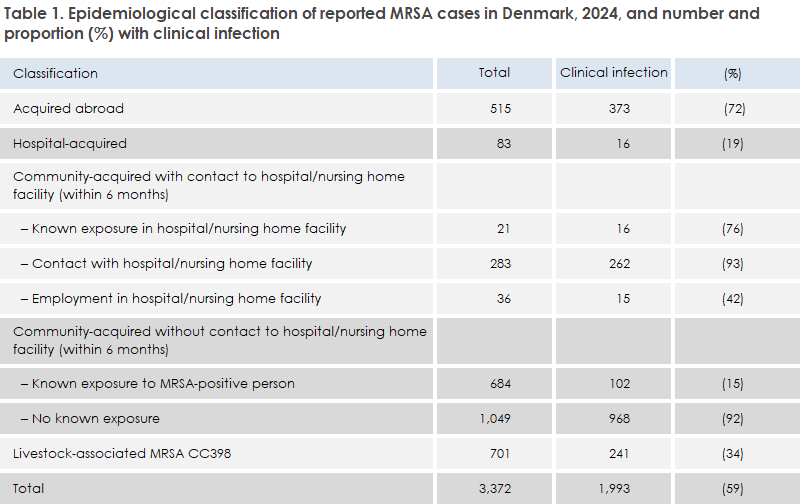
The majority of MRSA cases were acquired in Denmark (2,857), while foreign acquisition was reported for 515 cases (15%). During the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020–21, this proportion was lower, whereas before COVID-19 it ranged between 15% and 20%. The number of hospital-acquired MRSA cases was 83 (compared with 102 in 2023 and 55 in 2022), continuing to represent only a small share of all cases (2.5%). Community-acquired MRSA cases without hospital or nursing home sector contact accounted for 1,733 cases (51%) in 2024. Among these, 684 (39%) had known exposure to a person with MRSA.
The number of livestock-associated MRSA CC398 cases was 701, representing 21% of all MRSA cases. This is the lowest proportion since 2012, where it was 15%. The proportion peaked in 2014 at 43%. The decline in livestock-associated MRSA CC398 may reflect that surveillance covers only new cases, and that persons previously found positive therefore are not registered again. The prevalence in pig farms remains above 90%
Infections
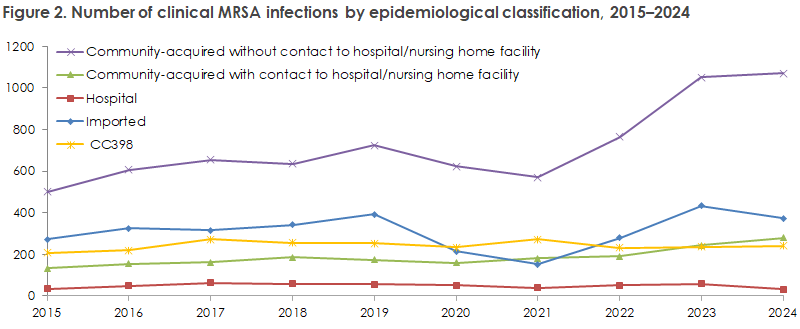
For 1,993 cases (59%), the reason for sampling was clinical infection. Most infections occurred among community-acquired cases without contact with hospitals or nursing homes (968) and among imported cases (373) (see Figure 2). MRSA was isolated from blood in 47 cases, corresponding to 1.9% of all S. aureus bacteremias, consistent with recent years. Among hospital-acquired cases, 16 patients (19%) had infections, and 15 healthcare workers (42%) were found infected with MRSA. The number of infections among imported cases decreased slightly from 434 in 2023 to 373 in 2024. For 102 cases of community-acquired infection, known exposure to MRSA was reported (see Table 1). The number of community-acquired infections with reported hospital or nursing home sector contact within the previous six months was 278 in 2024, the highest number recorded to date (see Figure 2).
Typing
MRSA type CC398 was detected by a specific PCR assay, which also determined whether the strain was the livestock-associated or the human variant (N=701 and N=43, respectively). Isolates with a characteristic livestock-MRSA CC398 profile were generally not spa-typed, whereas all other isolates were typed.
The remaining 2,671 isolates belonged to 403 different spa types, grouped into 26 clonal complexes (CC groups). The five most frequent were: t304/CC6 (N=288), t127/CC1 (N=210), t223/CC22 (N=138), t008/CC8 (N=135), t002/CC5 (N=129). These clones have been among the most widespread for several years.
Outbreaks
Statens Serum Institut offers whole-genome sequencing (WGS) of all isolates from outbreaks, providing more detailed characterization than spa typing alone. If an outbreak involves a clone within a common spa type, WGS can be an important tool for delimiting and understanding its extent.
Through the notification system, collaboration with local MRSA units, and typing of submitted isolates, a total of 38 outbreaks were identified in hospitals, nursing homes, and other institutions, comprising 191 MRSA cases, of which 86 were infections and 105 were found via screening or contact tracing. Most outbreaks involved 1 to 5 patients. The largest outbreak involved 43 patients and originated in a neonatal unit. Among the 38 outbreaks, four occurred in neonatal departments. Two of these had begun in earlier years, with additional patients identified in 2024. There were also 18 outbreaks in nursing homes or related nursing care services (48 patients) and eight outbreaks in other hospital departments (23 patients). An outbreak that began in 2023 in kindergartens, primarily causing impetigo among children, continued in 2024 with 26 new patients. The same MRSA subtype was observed in different parts of Denmark without a link to this outbreak and has been reported in 11 European countries.
Livestock-Associated MRSA CC398
The 701 cases of livestock-associated MRSA CC398 in 2024 represent the lowest number since 2013 (638 cases). A total of 241 (34%) had clinical infection at the time of diagnosis (see Table 1).
Contact with livestock, especially pigs, is the main source of MRSA transmission to humans.
Of all cases, 563 (80%) occurred in persons with direct contact with pigs or in their household members. The remaining 138 (20%) patients had no known contact with animals, and among these, 114 had clinical infections. The proportion of persons infected without known livestock contact remained consistent with recent years, indicating no significant new transmission routes of livestock-associated MRSA in Denmark. Most livestock-MRSA patients without animal contact are considered as community-acquired, with or without healthcare contact. In 2024, there were seven cases of bacteremia with livestock-MRSA CC398, one of whom died within 30 days after sampling.
MRSA can also occur in other animals than pigs, particularly horses and cattle, and rarely in poultry. The prevalence of MRSA in herds of these animals is much lower than in pig herds.
Moreover, hedgehogs are a natural reservoir for the mecC variant of MRSA. In 2024, findings of livestock-MRSA CC398 in humans with contact to animals other than pigs were limited to 20 patients with cattle contact, 12 with horse contact, and 1 with mink contact. Among the 66 mecC MRSA patients in 2024, five reported contact with animals (three with horses and two with pigs).
Imported MRSA
The number of imported cases was 515, slightly lower than in 2023 (574). This corresponds to 15% of all cases. Among imported cases, 109 (21%) had a history of hospitalization abroad.
This summary is also reported in EPI-NEWS 43b/2025.