No 43b - 2025
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) 2024
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) 2024
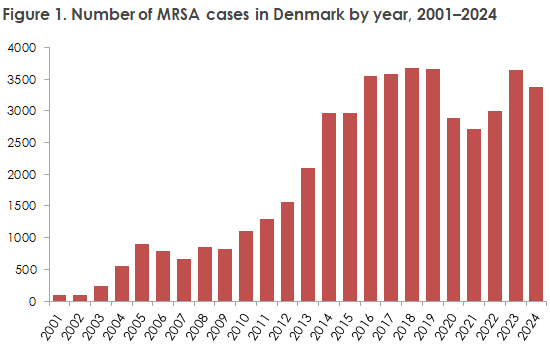
The number of new MRSA cases was 3,372 in 2024 (Figure 1), which was 8% lower compared with 2023 (3,649); EPI-NEWS 4/2025. Thus, the number was at the same level as in the years before the COVID-19 pandemic, during which the number had fallen by approximately 20%.
60% presented with symptomatic infections, the majority of which were skin and soft tissue infections.
There were 47 cases of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia (SAB) caused by MRSA in 2024, accounting for 1.9% of all SAB cases, which is a low proportion in an international context.
For a detailed epidemiological description of the occurrence in 2024, see the Annual Report on MRSA 2024.
In 2024, a total of 38 outbreaks were registered in hospitals, nursing homes, and other institutions, involving 191 MRSA cases. Four of the outbreaks occurred in neonatal units and included 76 cases.
Additionally, there were eight outbreaks in other hospital departments (a total of 23 patients) and 18 outbreaks in either nursing homes or associated home care services (48 cases). Despite these outbreaks in the healthcare system, the risk of acquiring MRSA infection in Danish hospitals remains low.
An outbreak that began in 2023 in kindergartens, primarily causing impetigo, continued in 2024 with 26 new patients. The same MRSA subtype was detected in different parts of the country without any link to this outbreak and has also been reported in ten other European countries.
The number of cases involving livestock-associated MRSA CC398 was 701, representing 21% of all new cases, the lowest proportion since 2012 (15%). In 2024, 114 persons without livestock contact developed infections with livestock-associated MRSA CC398. This is consistent with the previous year, and the spread of livestock-associated MRSA CC398 in the general population does not appear to be increasing.
In 515 cases (15%), MRSA was acquired abroad, corresponding to the proportion (15–20%) seen in the years before the COVID-19 pandemic and its related travel restrictions.
There were 1,070 community-acquired MRSA infections, representing the largest share of all MRSA infections (54%).
(A. Petersen, A.R. Larsen, Bacteria, Fungi and Parasites, T. Urth, Department of Infectious Disease Epidemiology and Prevention)