No 4 - 2025
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) 2023
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) 2023
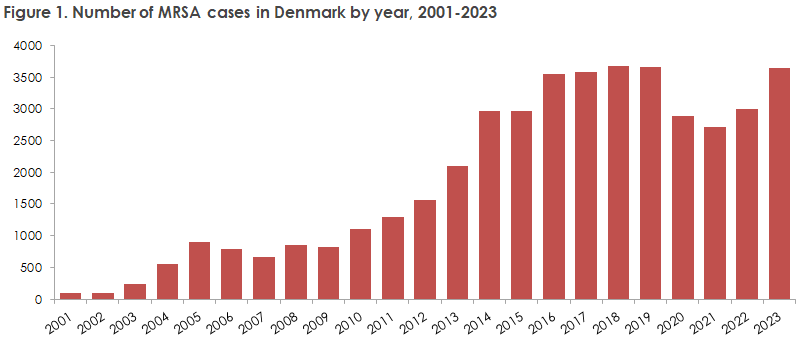
The number of new MRSA cases was 3,649 in 2023, Figure 1, which was 22% higher compared to 2022 (2,996), EPI-NEWS 34a/2023. Thus, the number was at the same level as in the years before the COVID-19 epidemic, during which the number dropped by approximately 20%.
For a detailed epidemiological description of the occurrence in 2023, refer to the annual report on MRSA 2023.
In 2023, a total of 41 outbreaks were registered in hospitals, nursing homes, and other institutions, encompassing 199 MRSA cases. Twelve of the outbreaks were in neonatal departments and included 81 cases. Additionally, there were six outbreaks in other hospital departments (a total of 15 patients) and 15 outbreaks either in nursing homes or associated home care (49 cases). The largest outbreak was linked to daycare centers and included a total of 32 children and parents, many of the children with impetigo.
The number of cases involving livestock-associated MRSA CC398 was 856, comprising 23% of the total number of cases, which has not been lower since 2012 (15%). In 2023, 117 individuals without contact with livestock acquired infections with livestock-associated MRSA CC398. This is at the same level as in previous years, and the spread of livestock-associated MRSA CC398 in the general population thus does not appear to be increasing.
There were 39 cases of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia with MRSA in 2023, comprising 1.5% of all cases.
In 574 cases (16%), MRSA was acquired abroad, corresponding to the proportion (15–20%) in the years before COVID-19 and the related travel restrictions.
Similarly, there was a significant increase in community-acquired MRSA infections, which can also be explained by the end of COVID-19 restrictions related to personal contact.
(A. Petersen, A.R. Larsen, Bacteria, Fungi, and Parasites, T. Urth, Department of Infectious Disease Epidemiology and Prevention)