No 48 - 2025
Vaccination with Vaxneuvance /
Mycoplasma genitalium in Denmark, 2024
Vaccination with Vaxneuvance
Statens Serum Institut wishes to draw attention to the fact that the switch to the 15-valent pneumococcal vaccine (PCV15/Vaxneuvance) in the childhood vaccination programme as of 1 November 2025, EPI-NEWS 43a/2025 , has led to an increased risk of simultaneous administration of PCV13 and PCV15, and in most cases without the child having received Pentavac.
This means that the child has both an increased risk of experiencing local adverse reactions at the injection sites and may also be missing Pentavac. In such cases, Pentavac should be administered as soon as possible after the parents have been informed.
Unintended administration of vaccines should always be reported as an unintended event (UTH) to the Danish Institute for Quality in Healthcare, which as of 1 May 2025 has taken over operation of the Danish Patient Safety Database (DSPD). Reports must be submitted to Unintended events .
(Advisory Team, Department of Infectious Disease Epidemiology and Prevention)
Mycoplasma genitalium in Denmark, 2024
Data from the Danish Microbiology Database (MiBa) show that the incidence of Mycoplasma genitalium (MG) in Denmark in 2024 remained at a stable level compared with the previous year EPI-NEWS 51, 2024. In total, 37,499 disease episodes were registered, representing a decrease of 10.6% compared with 2023, but with an overall unchanged positive rate of 11.6%. A total of 4,352 positive episodes were detected, distributed across 1,783 men and 2,569 women. Men had a higher positive rate of 14.7% compared with 10.1% among women. Since 2011, the positive rate has increased markedly from 6.1% to 11.6% and since 2020, MG has had a higher positive rate than chlamydia in Denmark, which in 2024 was 8.5%, Table 1.
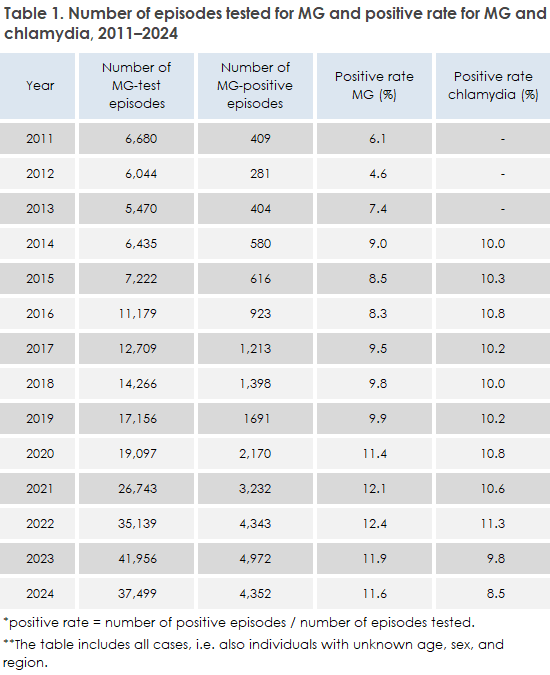
Most MG cases were observed among 20–24-year-olds, and both incidence and positive rates were highest in this age group for both sexes. Men aged 20-24 years had a positive rate of 21.9%, while women in the same age group were at 14.7%. The highest MG incidence is seen in slightly older age groups compared to chlamydia, where the highest rates are found among 15-19-year-olds. In general, testing activity was higher among women than men. In 2024, 846 tests per 100,000 inhabitants were performed for women compared to 410 for men.
The geographical distribution shows that the highest testing activity continues to be found in Copenhagen City and Greater Copenhagen suburbs, where the incidence among women was 2,889 and 1,183 per 100,000 inhabitants, respectively, in 2024. A decline was observed in both, testing activity and positive rate in Copenhagen, while the level for the rest of the country remained relatively unchanged. Overall, testing activity decreased from 2023 to 2024 for both sexes. Although the overall positiverate was unchanged between the two years, a small decrease was seen among men from 16.5% to 14.8%, while the rate among women remained unchanged at around 10%.
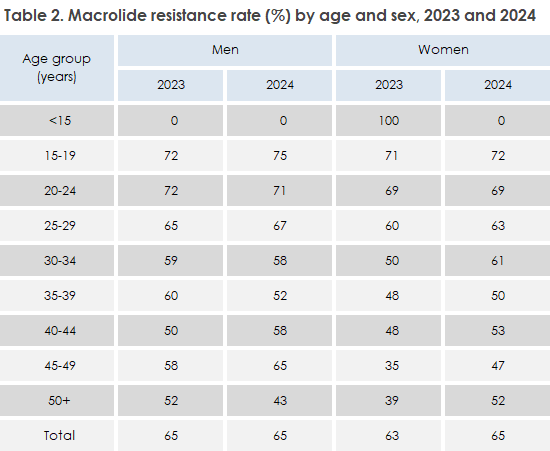
Treatment of MG follows the European guidelines from IUSTI, WHO and ECDC. Treatment is complicated by increasing antibiotic resistance, especially to macrolides. Resistance testing is therefore recommended before treatment with macrolides. In 2024, the macrolide resistance rate was mostly unchanged compared to 2023, at 65% in men (65% in 2023) and 65% in women (63% in 2023), Table 2. The highest resistance rates were seen among young people aged 15-24 years, where almost three out of four detections in this age group had macrolide resistance mutations (MRM), Table 2. Resistance to macrolides in MG is associated with the use of azithromycin for the treatment of uncomplicated chlamydia. Following the 2018 recommendation by the SSI to replace azithromycin with doxycycline for the treatment of uncomplicated chlamydia, the use of azithromycin has fallen markedly from 29,025 prescriptions in 2019 to 11,545 in 2024, while doxycycline use has increased from 1,515 prescriptions in 2019 to 17,660 prescriptions in 2024 for chlamydia/ MG indications.
A sample of 473 MG-positive specimens were investigated for quinolone resistance markers, which were found in 7.2% of tested patients in 2024. This is a slight increase from 6.3% in 2023. The resistance rate remained unchanged among men (7.7%), but a small increase was seen among women from 5.2% to 6.9%. The occurrence of double-resistant strains, resistant to both macrolides and quinolones, increased from 5.8% to 6.8%. The most commonly detected quinolone-resistance associated mutations (QRAM) were S83I and D87N, as previously reported.
The overall trend for MG in Denmark shows an unchanged positive rate and an unchanged, but high macrolide resistance rate, along with a slightly increasing quinolone resistance rate. According to data from the Prescription Registry, azithromycin still accounts for approximately 60% of the prescriptions issued for chlamydia treatment in 2024. This should be reduced further, especially since no effective and easily accessible alternative for MG treatment is yet available. It must also be emphasized that testing for MG should only be performed when symptoms are present.
(S.T. Drud, T.R. Pedersen, J.S. Jensen, Section for Reproductive Microbiology, Bacteria, Parasites and Fungi)