No 49 - 2024
Gonorrhea 2023
Gonorrhea 2023
- 5,579 cases of gonorrhea were registered in the Danish Microbiological Database (MiBa).
- 4,205 cases were reported to the Notification System for Infectious Diseases.
- Women accounted for 35% of all cases, and men accounted for 65%.
- Men who have sex with men (MSM) continued to represent the largest proportion of cases.
- Information on HIV status was available for 1,975 (47%) of the reported gonorrhea cases. Among 1,326 cases in MSM with known HIV status, 163 (12%) were HIV-positive.
- 25 (1.3%) women reported with gonorrhea were pregnant.
- There was a decrease in the number of gonorrhea cases among 15-19-year-olds and an increase, especially among men aged 30-39 and 50+ years.
The national surveillance of gonorrhea in Denmark, conducted by Statens Serum Institut (SSI), is based on data from the Danish Microbiological Database (MiBa) and clinical reports via the SEI2 system.
MiBa collects analysis results for both culture and nucleic acid amplification techniques (NAAT) from all Departments of Clinical Microbiology. All these departments perform combined tests for gonococci and Chlamydia trachomatis. A new case of gonorrhea is defined as having more than 21 days between positive samples from the same person, or if gonococci cultured within a shorter interval, have different resistance patterns. A negative episode is also defined by 21 days between negative findings.
In addition to laboratory-based surveillance, it is mandatory for doctors to report cases of gonorrhea to the Notification System for Infectious Diseases, which has been done electronically since 2022. The notification system collects information such as mode of transmission, sexual orientation, country of infection, and HIV status, which are not included in laboratory data. Therefore, it is important that all cases of gonorrhea are reported, as this provides essential epidemiological knowledge that enables health authorities and professionals to implement targeted preventive measures. In 2023, 75% of cases were reported via SEI2.
A more detailed account of gonorrhea in 2023 can be seen in the Annual Report.
Again this year, Statens Serum Institut was present at the Folkemødet, where there were presentations on the general increase in sexually transmitted infections seen in Denmark in recent years and what can/should be done about it. The Danish Health Authority, Sex & Samfund, and the AIDS Foundation, together with Statens Serum Institut, participated in a panel discussion to discuss possible measures. The main points were that new thinking is needed in terms of prevention, as the old "scare campaigns" from the AIDS epidemic are no longer relevant. As sexually transmitted infections are increasing, especially among the very young, prevention needs to be inclusive and relevant. The increased international prevalence of antibiotic resistance and the potential consequences of an infection (e.g., pelvic inflammatory disease and epididymitis) are particularly concerning.
In 2023, 5,579 cases of gonorrhea were registered in MiBa, an increase of 6% compared to 2022, but with a stable positivity rate of 1.4%. The distribution was 35% cases among women and 65% among men, similar to 2022. Among men, as in previous years, the majority of cases were among men who have sex with men (MSM), as shown in Figure 1.
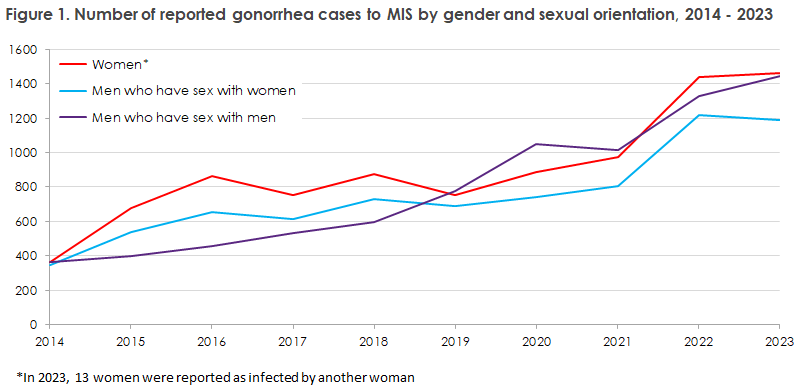
In 8% of cases, the country of infection was reported as being outside Denmark. The most frequent countries were Spain, Thailand, and Germany.
The largest increase in the number of gonorrhea cases was observed among men aged 30-39 and 50+ years. Among both men and women, the incidence among 15-19-year-olds decreased, which was also observed for chlamydia (EPI-NEWS 35/2024). It is not known whether the decrease among young people is due to targeted campaigns, increased awareness of sexually transmitted infections in general, or is coincidental.
More women were tested in all age groups, except for those aged 50+, compared to men. The highest testing frequency was among those aged 20-24, but men generally had a higher positivity rate than women.
There were no significant differences in the incidence of gonorrhea across regions. The highest incidence was in Copenhagen, with a significantly higher positivity rate among men.
In 2023, seven cases of gonorrhea were registered among individuals under 15 years old, including a few cases of mother-to-child transmission during birth.
There were 21 cases of gonorrhea registered among transgender individuals, an increase from six cases in 2022. This increase is not necessarily due to a real rise in cases but rather increased awareness of correct registration by both reporting doctors and SSI.
Among the reported cases in 2023, 4% had known HIV, and less than 0.1% had newly acquired HIV. Of the HIV-negative MSM, 59% were on PrEP treatment to prevent HIV transmission. It is noted that the target groups for receiving PrEP according to the Danish Health Authority's recommendations are:
- Individuals belonging to the group of MSM or the group of trans women or trans men who have sex with men (the following criteria can be used as guidelines for risk behavior) and:
- The person has had unprotected anal intercourse with at least two male partners within the last 12 weeks (a known HIV-negative steady partner is not counted)
- The person has had syphilis within the last 24 weeks
- The person has had chlamydia or gonorrhea within the last 24 weeks
In 2023, 2,660 isolates of Neisseria gonorrhoeae were submitted to SSI as part of the national resistance surveillance. An increase in resistance to azithromycin and a slight increase in ciprofloxacin resistance were observed. Ceftriaxone resistance has not been recorded since 2017.
Overall, national surveillance shows that the incidence of gonorrhea in Denmark is moderately increasing, and resistance development continues to require monitoring to ensure effective treatment.
(T.R. Pedersen, S. Hoffmann, Department of Bacteria, Parasites & Fungi, M. Wessman, C. Eves, Department of Infectious Disease Epidemiology and Prevention, L. Nielsen, S.F. Ravn, N. Bindslev, Data Integration and Analysis)