No 50 - 2023
Gonorrhoea 2021 - 2022
Gonorrhoea 2021 and 2022
For a detailed epidemiological description of the incidence in 2021 and 2022, please see the 2021 & 2022 Annual Gonorrhoea Report.Gonorrhoea diagnosed in 2021
- A total of 3,570 cases of gonorrhoea were recorded in the Danish Microbiology Database (the MiBa).
- In all, 2,805 cases were notified to the Notification System for Infectious Diseases (NSID); hereof 1,856 among men and 949 among women, distributed among a total of 2,637 persons.
- Among men, 1,015 (55%) were notified as homosexual transmissions. The corresponding number for women was 20 (2%).
- Information about HIV status was available for 2,210 (79%) of the notified gonorrhoea cases. Among 959 cases in MSM, 134 (14%) were HIV positive
- A total of 22 (2%) of the women notified with gonorrhoea were pregnant.
- The most frequently occurring age group was 30-39 years for men and 15-19 years for women. The City of Copenhagen was the area where most cases occurred in men, and East Jutland was the area where most cases occurred in women.
Gonorrhoea diagnosed in 2022
- A total of 5,204 gonorrhoea cases were recorded in the MiBa.
- In all, 3,916 cases were notified to the NSID; hereof 2,538 among men and 1,378 among women, distributed among a total of 3,655 persons. This constituted a 46% increase compared with 2021.
- Among men, 1,308 (52%) were notified as homosexual transmissions. The corresponding number for women was 22 (2%).
- Information about HIV status was available for 2,189 (56%) of the notified gonorrhoea cases. Among 1,210 cases in MSM, 200 (17%) were HIV positive
- A total of 23 (2%) of the women notified with gonorrhoea were pregnant.
- The most frequently occurring age group was 30-39 years for men and 20-24 years for women, and the City of Copenhagen was the area where most cases occurred.
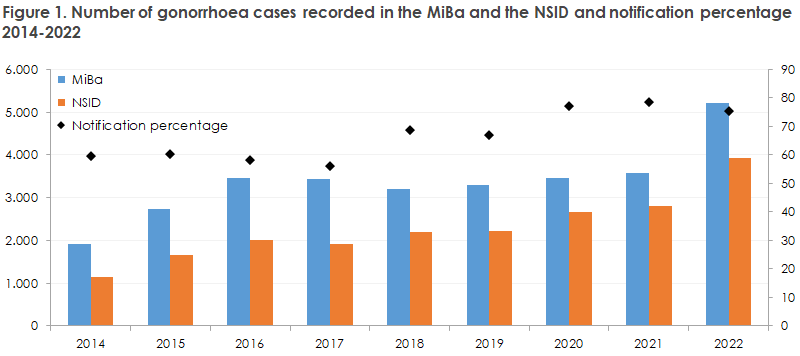
The number of gonorrhea cases has followed an increasing trend for a number of years, but the increase recorded from 2021 to 2022 was exceptionally steep (46%). The strong increase recorded may, among others, be due to the partial lifting of COVID-19 restrictions, but mainly, of course, to an increased occurrence of condom-free sex.
Unfortunately, the introduction of electronic notification via the electronic notification system (SEI) of the Danish Health Data Authority in 2022 has not heightened the notification percentage, Figure 1. Gonorrhoea notification is statutory, and - to ensure a robust and credible monitoring that may be used to prevent disease - it is still necessary to keep in place both laboratory surveillance and epidemiological monitoring.
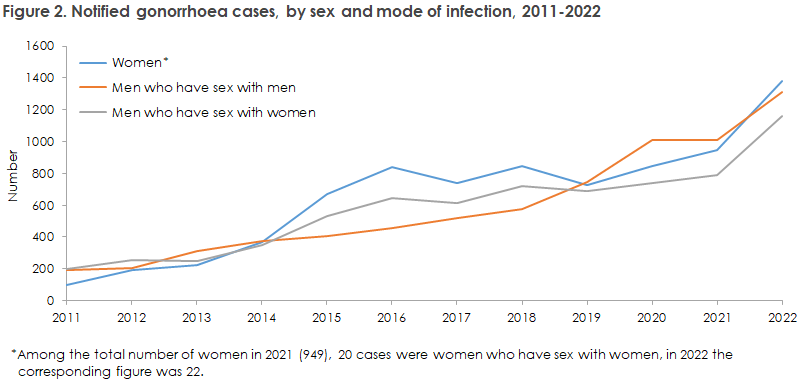
The increase in the number of gonorrhoea cases is greatest among young heterosexual men and women, but is also seen among homosexual men, Figure 2. However, the occurrence of gonorrhoea remains considerably higher among homosexual men than among heterosexual men and women (20 times higher when taking into account that approx. 5% of the male population are homosexually active).
If you have had sex with a new partner without using a condom, it is important to be tested. And if you are diagnosed with gonorrhoea (or any other sexually transmitted disease), you need treatment and should contribute to informing any sexual partners. The infectious chain may be broken only by using a condom and ensuring rapid infection tracing and relevant treatment. Gonorrhoea of the pharynx and rectum are generally low or asymptomatic. If the infection is located to these anatomical sites exclusively and if it is not diagnosed and treated, the patient constitutes an infection reservoir.
In the MiBa, the 2021-2022 period recorded 30 gonorrhoea cases among 28 children below 15 years of age.
Only 16 of the 28 children registered in the MiBa were also notified with the NSID.
Healthcare workers are encouraged to be particularly attentive to gonococci as a cause of conjunctivitis in neonates – especially in the first two weeks of life. Gonococcal conjunctivitis, which is not exclusively seen in neonates, is a potentially very serious condition that may cause destruction of the eyeball if it goes untreated.
These patients must therefore be referred urgently to a specialised department to ensure that correct and immediate eyesight-preserving treatment is initiated.
The prevalence of ciprofloxacin resistance increased slightly. The drug may be used once susceptibility has been confirmed, see the 2021-2022 Annual Gonorrhoea Report.
(S. Cowan, M. Wessman, Department of Infectious Disease Epidemiology and Prevention, K.D. Bjerre, the Data Integration and Analysis Secretariat, T. Roland Pedersen, A. Skafte-Holm, S. Hoffmann, Department of Bacteria, Parasites & Fungi)
13 December 2023